Selected Publications
Miikka Silfverberg and Mans Hulden (2018). An Encoder-Decoder Approach to the Paradigm Cell Filling Problem (PDF).
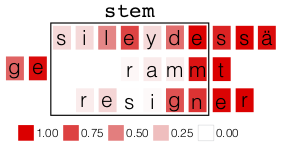 The Paradigm Cell Filling Problem in morphology
asks to complete word inflection tables
from partial ones. We implement novel
neural models for this task, evaluating them on
18 data sets in 8 languages, showing performance
that is comparable with previous work
with far less training data. We also publish a
new dataset for this task and code implementing
the system described in this paper.
The Paradigm Cell Filling Problem in morphology
asks to complete word inflection tables
from partial ones. We implement novel
neural models for this task, evaluating them on
18 data sets in 8 languages, showing performance
that is comparable with previous work
with far less training data. We also publish a
new dataset for this task and code implementing
the system described in this paper.Miikka Silfverberg, Lingshuang Jack Mao and Mans Hulden (2018). Sound Analogies with Phoneme Embeddings (PDF, poster). Inaugural Meeting of SCIL
 Distributional models of
words in NLP—word embeddings—have recently been shown to
reliably encode semantic information. We study how well corresponding
distributional properties carry over to similarly learned phoneme
embeddings, that is, whether phoneme vector spaces align with
phonetic features such as +/-voiced and +/-back. This
paper demonstrates a statistically significant correlation between
phonetic feature spaces and purely distributionally learned vector
spaces of phonemes.
Distributional models of
words in NLP—word embeddings—have recently been shown to
reliably encode semantic information. We study how well corresponding
distributional properties carry over to similarly learned phoneme
embeddings, that is, whether phoneme vector spaces align with
phonetic features such as +/-voiced and +/-back. This
paper demonstrates a statistically significant correlation between
phonetic feature spaces and purely distributionally learned vector
spaces of phonemes.Miikka Silfverberg, Adam Wiemerslage, Ling Liu and Lingshuang Jack Mao (2017). Data Augmentation for Morphological Reinflection (PDF, poster). CoNLL-SIGMORPHON 2017 Shared Task: Universal Morphological Reinflection
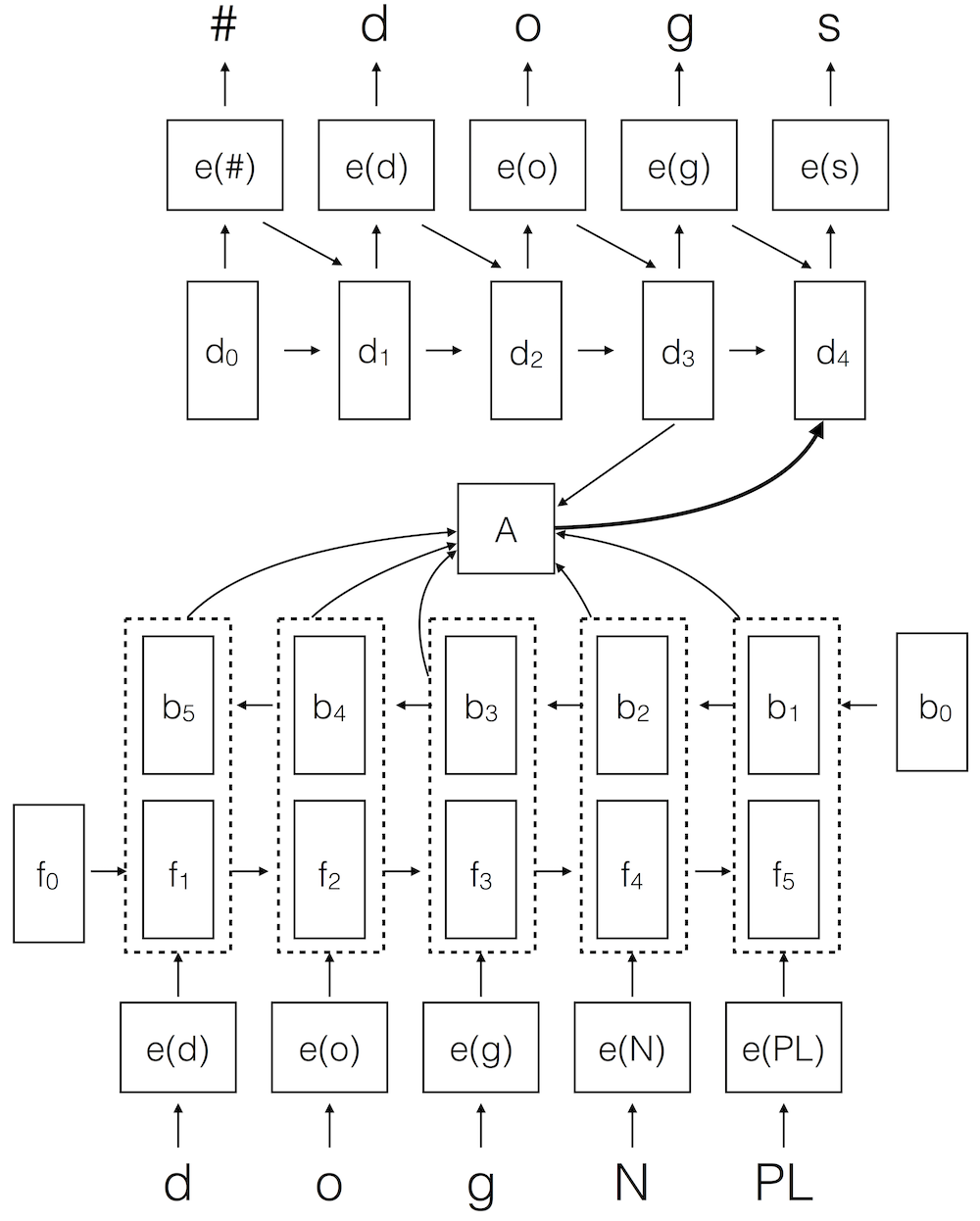 This paper presents the submission of the CU Boulder
Linguistics team for the 2017 CoNLL-SIGMORPHON shared task on morphological
reinflection. The system is an RNN Encoder-Decoder model which is
specifically geared toward a low-resource setting. To this end, it
employs data augmentation to counteract overfitting and a copy symbol
for processing characters unseen in the training data. The system is
tested on the reinflection task for 52 languages using three data
settings low (100 training examples), medium (1000 training examples),
and high (10,000 training examples). The experiments show that data
augmentation allows the system to learn models even in low resource
settings which are very challenging for traditional RNN
encoder-decoder systems.
This paper presents the submission of the CU Boulder
Linguistics team for the 2017 CoNLL-SIGMORPHON shared task on morphological
reinflection. The system is an RNN Encoder-Decoder model which is
specifically geared toward a low-resource setting. To this end, it
employs data augmentation to counteract overfitting and a copy symbol
for processing characters unseen in the training data. The system is
tested on the reinflection task for 52 languages using three data
settings low (100 training examples), medium (1000 training examples),
and high (10,000 training examples). The experiments show that data
augmentation allows the system to learn models even in low resource
settings which are very challenging for traditional RNN
encoder-decoder systems.Miikka Silfverberg and Mans Hulden (2017). Weakly Supervised Learning of Allomorphy (PDF, poster). SCLEM
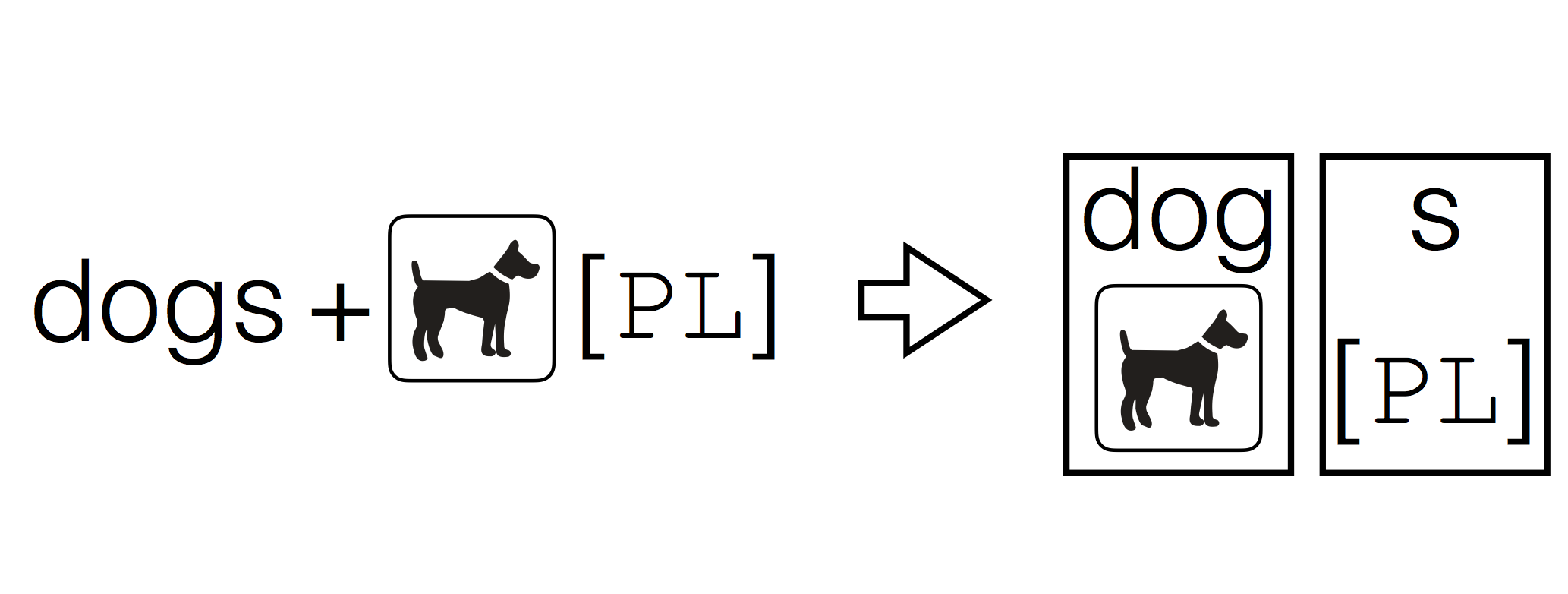 Most NLP
resources, that offer annotations at the word segment level, provide
morphological annotation that includes features indicating tense,
aspect, modality, gender, case, and other inflectional information.
Such information is, however, rarely aligned to the relevant parts of
the words. In this paper, we explore several methods to learn this
latent alignment between parts of word forms and the grammatical
information provided.
Most NLP
resources, that offer annotations at the word segment level, provide
morphological annotation that includes features indicating tense,
aspect, modality, gender, case, and other inflectional information.
Such information is, however, rarely aligned to the relevant parts of
the words. In this paper, we explore several methods to learn this
latent alignment between parts of word forms and the grammatical
information provided.Miikka Silfverberg, Teemu Ruokolainen, Krister Lindén and Mikko Kurimo (2016). FinnPos: An Open-Source Morphological Tagging and Lemmatization Toolkit for Finnish (PDF). Language Resources and Evaluation 50 (4)
Miikka Silfverberg, Teemu Ruokolainen, Krister Lindén and Mikko Kurimo (2014). Part-of-Speech Tagging using Conditional Random Fields: Exploiting Sub-Label Dependencies for Improved Accuracy (PDF). ACL
Software
FinnPos is a morphological tagging and lemmatization toolkit for morphologically rich languages such as Finnish. It is based on the averaged perceptron framework and features
- State-of-the-art tagging accuracy.
- Fast estimation and application.
- Support for large label sets exceeding 1000 label types.
- An option to use taggers for morphological disambiguation.
- Data driven lemmatization for OOV words.
- Feature extraction using sub-labels of structured morphological labels (e.g. “Noun+Plural+Nominative”).
- Customizable feature extraction.
FinnPos is implemented by myself and Teemu Ruokolainen.
The Helsinki Finite-State Transducer toolkit is intended for processing natural language morphologies. The toolkit is demonstrated by wide-coverage implementations of a number of languages of varying morphological complexity.
I implemented and helped design several component of HFST. One of
the most prominent components is hfst-twolc which is a compiler
for two-level phonological rules.